
What is the Harmonized System (HS) Code?
The Harmonized System (HS) codes are a crucial element in international trade. These codes help classify products and ensure smooth customs processes across borders.
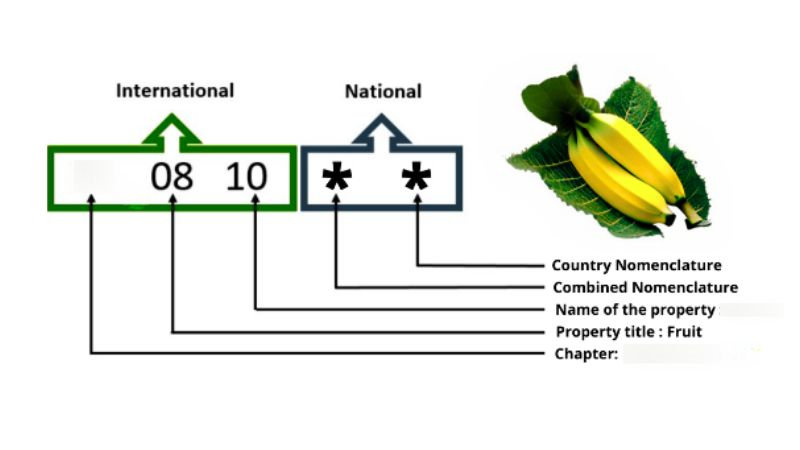
An HS code typically consists of six digits. These numbers are standardized globally, making it easier for customs officers to identify and classify goods. Here’s a breakdown of what each part of the HS code signifies:
- First two digits: Represent the HS Chapter, indicating the broad category a product belongs to.
- Third and fourth digits: Indicate the heading within that Chapter, specifying the product type.
- Last two digits: Show the subheading, detailing the specific item.
Countries might add more digits to these six for more detailed classification. For instance, the United States uses a 10-digit code known as the Schedule B number for exports.
How to Get an HS Code for Your Product?
Let’s go through the steps to obtain an HS code for “bananas” as an example.
- Understand the Product:
- Product: Bananas
- Form: Fresh
- Use: Consumption as fruit
- Familiarize Yourself with the HS Code Structure:
- HS codes usually have 6 digits that are internationally standardized, with additional digits that may vary by country.
- Use Online Tools and Resources:
- Visit the World Customs Organization (WCO) website or your country’s official customs website to access HS code lookup tools.
- Consult the HS Nomenclature:
- The HS nomenclature is a structured list of all product classifications. Browsing this can help find the appropriate code.
- Use Description Search:
- Enter a detailed description of the product into an online HS code lookup tool. For example, you’d enter “fresh bananas.” Based on the search results, this code is relevant for fresh bananas: HS Code 0803.90.10: Fresh bananas (other than plantains).
- Seek Expert Help:
- If you’re unsure, consult a customs broker, trade consultant, or contact your customs authority.
- Verify and Confirm:
- Once you have a potential HS code, cross-reference it with official resources or confirm with customs authorities.
HS Codes Usage in International Trade

To start, every product you ship needs an HS code. This is a standardized numerical system developed by the World Customs Organization.
Understand Tariffs and Duties: Each HS code is linked to a specific tariff rate. For fresh or chilled beef, the tariff could be 25%.
Input the Code on Shipping Documents: Include the HS code on all shipping and import documents. This ensures customs officials can quickly identify the product.
Using the correct HS code helps avoid delays at customs. It also ensures that you pay the right tariffs and taxes. A wrong code may lead to higher import tariffs or fines.
Remember, these codes are crucial for clear communication between you, customs officials, and trade authorities. Keep a handy list of your product’s HS codes for easy reference.
Common Terms:
- Customs Tariff: A tax on imports and exports between countries.
- Duties and Taxes: Fees imposed by the government on imported goods.
- Traded Products: Goods that are imported or exported for sale.
Using HS codes correctly saves you time and money, making international shipping smoother and more efficient.
HS Codes, HTS Codes, and Schedule B Codes: What is the Difference?
When you’re shipping products internationally, understanding the differences between HS, HTS, and Schedule B codes is crucial. These codes help classify products for various purposes such as tariffs, statistics, and customs regulations.
HS Codes (Harmonized System Codes): These are six-digit codes used globally to classify traded products. They are developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO) and form the basis for both HTS and Schedule B codes.
HTS Codes (Harmonized Tariff Schedule Codes): HTS codes are used by the United States for importing goods. They start with the same six digits as HS codes but include four more digits to give a full ten-digit number. These additional digits specify the product further and are used by the U.S. International Trade Commission (ITC).
Schedule B Codes: These are ten-digit codes used by the U.S. Census Bureau to track exports. Like HTS codes, the first six digits match the HS code, but the last four digits are specific to U.S. exports. These are often updated, either annually or semi-annually.
Each type of code serves a different purpose in the shipping and customs process, so knowing which one to use and when is essential for smooth international shipping operations. Here’s a quick reference:
- HS Codes: Global use, six digits
- HTS Codes: U.S. imports, ten digits
- Schedule B Codes: U.S. exports, ten digits
The Global Reach of the Harmonized System
The Harmonized System (HS) codes play a crucial role in international trade by providing a standardized method for classifying products. The use of HS codes extends across many countries and significantly impacts e-commerce.

More than 200 countries, including the United States, the European Union, China, Australia, and Japan, use HS codes to streamline customs processes and gather trade statistics.
In e-commerce, accurate HS codes are vital. They ensure correct tariff applications and reduce delays at customs. This helps your business avoid unexpected costs and ensures smooth delivery to international customers.
E-commerce platforms are increasingly integrating HS codes into their systems. This integration helps automate the classification of goods, facilitating faster shipping and better tracking of global trade trends. Proper use of HS codes also supports compliance with international shipping regulations, further enhancing your customer experience and business efficiency.
